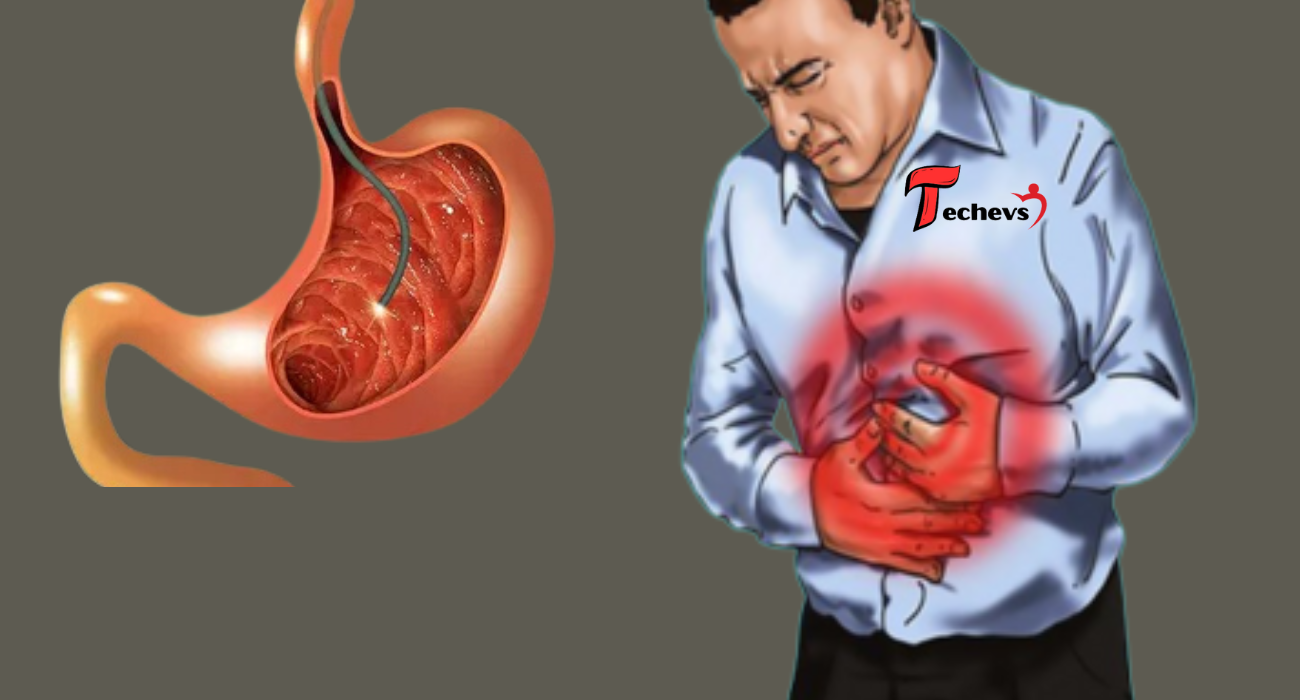
Stomach cancer ..here are the signs and symptoms
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a disease that originates in the stomach. Located in the upper middle of the abdomen, just below the ribs, the stomach plays a key role in breaking down and digesting food.
This cancer can develop in any area of the stomach. While globally, stomach cancer most often affects the main part of the stomach (the body of the stomach), in the United States it is more common for cancer to start at the gastroesophageal junction. This is the area where the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach, meets the stomach.
Doctors consider a variety of factors when developing a treatment plan, including where the cancer originated, the stage of the cancer, and the type of cells involved. Treatment usually involves surgery to remove the tumor, sometimes with additional medications before surgery.
The outlook for stomach cancer is more promising when it is confined to the stomach. If cancer is detected early and remains localized, small tumors have a good chance of being successfully treated, and many patients can expect to recover. However, most stomach cancers are diagnosed at an advanced stage, making treatment difficult. When cancer spreads outside the stomach or through its wall, it becomes more difficult to treat.
Symptoms
Symptoms of stomach cancer may include:
Difficulty swallowing
Abdominal pain
Bloating after eating
Feeling full after eating a small amount of food
Loss of appetite
Heartburn
Indigestion
Nausea
Vomiting
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Black stools
If symptoms do occur, they may include indigestion and upper abdominal discomfort. In advanced stages, more severe symptoms may occur, including fatigue, significant weight loss, vomiting blood, and black stools.
If the cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is called metastatic stomach cancer, and symptoms vary depending on where the cancer has spread. For example, if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, it can cause lumps under the skin. If it has reached the liver, it can cause jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes. If it has spread to the abdomen, fluid can build up, causing swelling.
When to see a doctor
Seek medical attention if you have any worrisome symptoms. Many conditions can cause symptoms similar to those of stomach cancer. Your doctor may perform tests to rule out other causes before diagnosing stomach cancer.
Causes
Although the exact cause of stomach cancer is still unclear, it is thought to begin when something damages the lining of the stomach. Possible risk factors include stomach infections, long-term acid reflux, and a diet high in salty foods. However, not everyone with these risk factors will develop stomach cancer, and more research is needed to better understand the origins of the disease.
Stomach cancer begins when stomach cells become damaged, leading to changes in their DNA. DNA carries the instructions that control how cells work, and when these instructions change, the cells begin to multiply uncontrollably. These mutated cells can live longer than normal cells, leading to the accumulation of cells that form a tumor.
As the cancer progresses, it can invade healthy tissue and grow deeper into the stomach wall. Over time, cancer cells can break away from the tumor and spread to other parts of the body, a process called metastasis.
Types of Stomach Cancer
The type of stomach cancer is determined by the type of cell in which the cancer started. Some common types:
Adenocarcinoma: The most common form of stomach cancer, arising from the mucus-producing cells of the stomach.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): These tumors begin in the nerve cells in the lining of the stomach and other digestive organs. GISTs are a form of soft tissue sarcoma.
Carcinoid tumors: These cancers develop in neuroendocrine cells, which perform functions related to both nerve cells and hormone-producing cells.
Lymphoma: Lymphomas are cancers that begin in cells of the immune system and can sometimes develop in the stomach. This usually happens when the body sends immune cells to the stomach to fight an infection. Most gastric lymphomas are classified as non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing stomach cancer, including:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus
A diet high in salty and smoked foods
A diet low in fruits and vegetables
A stomach infection..